Harnessing the Power of Ice Therapy!
If you’re an athlete or fitness enthusiast, you know that pain and inflammation can often hold you back from achieving your full potential. While there are many strategies for reducing pain and speeding up recovery, one of the most effective and accessible is ice therapy.
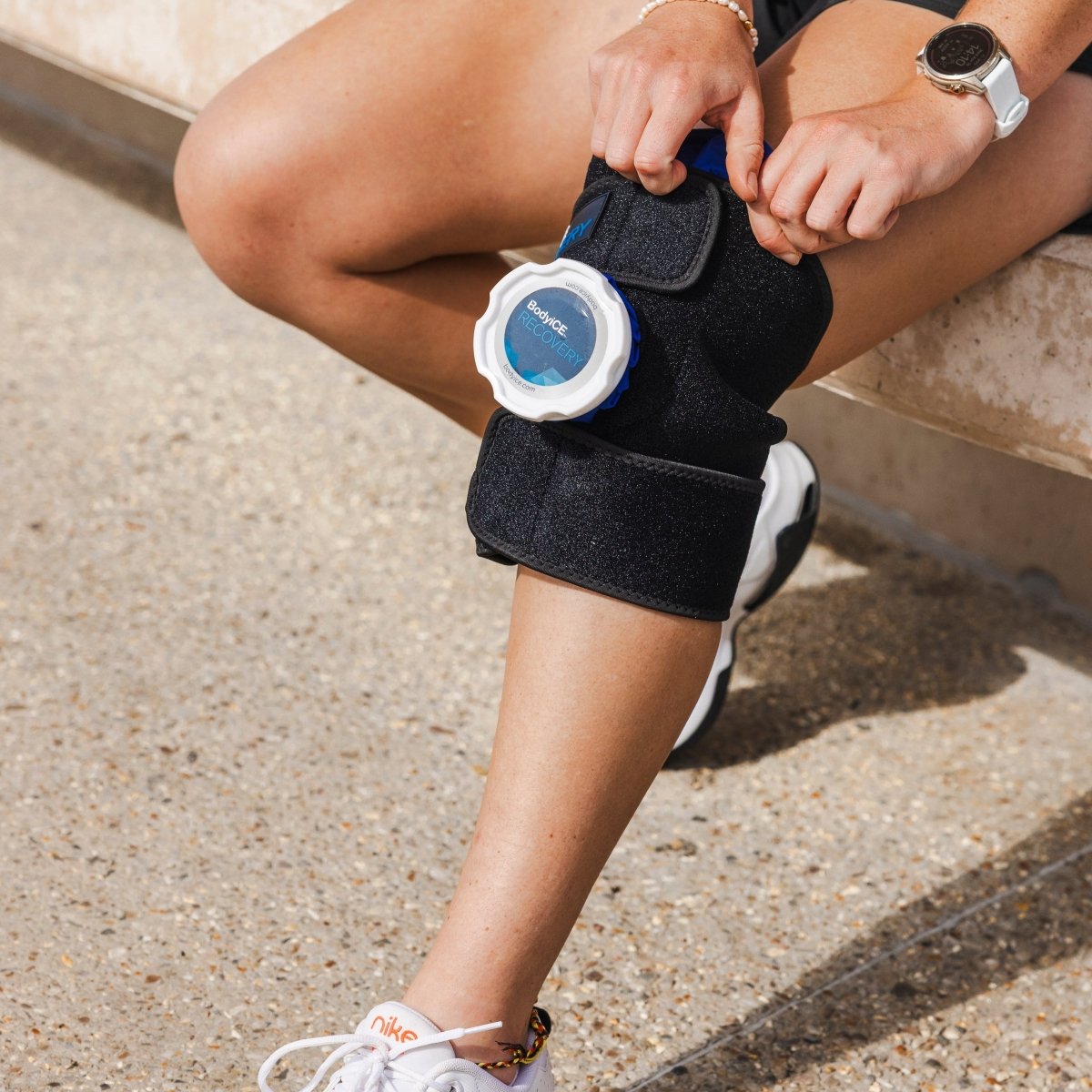
Ice therapy, also known as cryotherapy, involves applying cold to the body to reduce inflammation and pain. This can be done using ice packs, cold baths, or even whole-body cryotherapy chambers. But how does ice therapy actually improve performance? Let’s take a closer look.

Reduces Inflammation:
Inflammation is the body's natural response to injury or stress, but it can also be a barrier to performance. When you have inflammation in your muscles or joints, it can cause pain, stiffness, and decreased range of motion. This can make it harder to train effectively and can lead to decreased performance over time. Icing can help to reduce inflammation by cooling the affected area and constricting blood vessels, which can help to limit the swelling and soreness associated with inflammation.
Speeds Up Recovery Time:
Recovery is a crucial part of training, and it can make a big difference in your overall performance. When you use ice therapy to cool down after a workout, it can help to speed up your recovery time. The cold temperature can help to reduce the metabolic rate of your cells, which can help to reduce inflammation and promote healing. Additionally, ice therapy can help to flush out waste products and increase blood flow to the affected area, which can bring more nutrients and oxygen to the muscles and joints, helping them recover faster.
Enhances Circulation:
While ice therapy constricts blood vessels at first, it can also help improve circulation in the long run. As the body warms up after ice therapy, blood flow to the affected area increases, delivering fresh oxygen and nutrients to help repair and rebuild muscle tissue.
Prevents Injury:
Injuries are a common occurrence in sports, and they can be a major setback for athletes. Using cryotherapy as a preventative measure can help to reduce your risk of injury. By cooling down your muscles and joints before and after a workout, you can help to reduce the risk of muscle strains, sprains, and other injuries. Additionally, ice therapy can help to improve your range of motion and flexibility, making it easier for you to move through your exercises without putting too much strain on your muscles and joints.
Boosts Mental Toughness:
Ice therapy can also have a psychological benefit, helping athletes to develop mental toughness and resilience. By exposing themselves to cold temperatures and uncomfortable sensations, athletes can learn to push through discomfort and stay focused on their goals
Improves Performance:
Ultimately using cryotherapy can help to improve your performance by allowing you to train harder and recover faster. When you're able to push yourself to your limits without fear of injury or inflammation, you can make more progress and see better results. Additionally, by reducing your recovery time, you can train more frequently and consistently, which can help to improve your overall fitness level.

Cryotherapy can be a powerful tool for athletes looking to improve their performance. Whether you're training for a competition or just trying to reach your personal goals, ice therapy can help you recover faster, prevent injury, and push yourself harder than ever before.
So, next time you're gearing up for a workout, consider adding BodyICE to your routine and see how it can help you take your performance to the next level.




















Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.